Basics of Nuclear
Benefits of Nuclear
Fights Climate Change

Canadian nuclear reactors produce continuous 24/7 CO2-free power that fights climate change! 60% of Ontario’s electricity and 40% of New Brunswick’s! [1, 2]
Canadian design, production, and fuel

Canadian reactors: designed in Canada by Canadians and most of the parts are from Canada. With the uranium fuel mined in Saskatchewan! [3]
Isotopes for diagnosis and treatment

Not only did Canada invent Co60 treatment used to treat cancer but thanks to recent innovation we can now produce this life-saving isotope in our nuclear power plants! [4]
How does a nuclear reactor work?
A nuclear reactor produces heat to make steam. Just like the steam from a kettle below, the pressure from steam can make motion, which can create electricity. Splitting nuclei makes heat from uranium rather than burning fossil fuels; so nuclear power emits no CO2! This steam spins a turbine, moves magnets to generate electricity for Canadian homes.
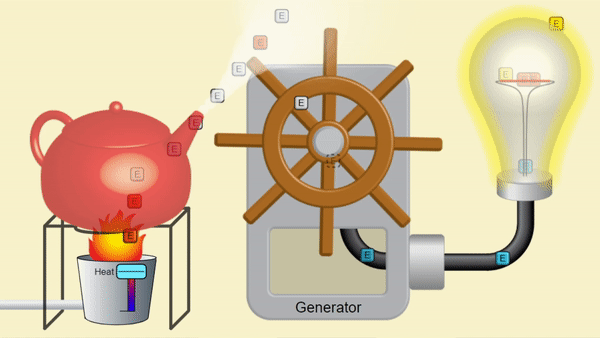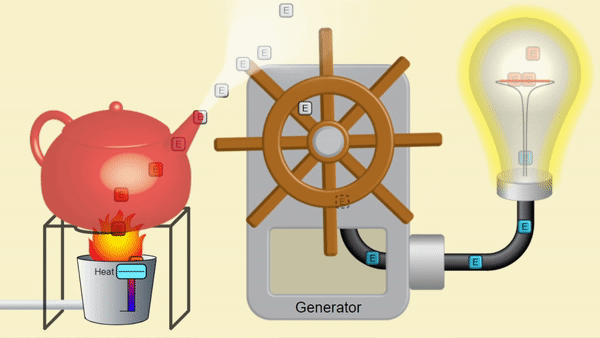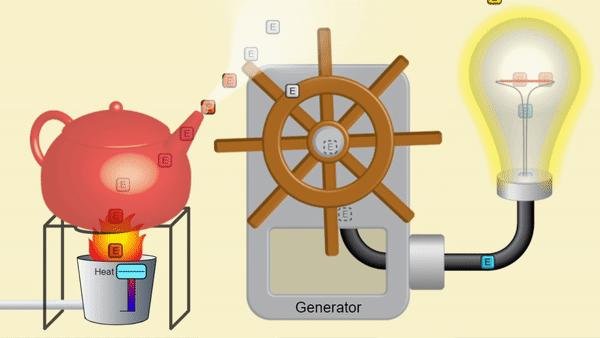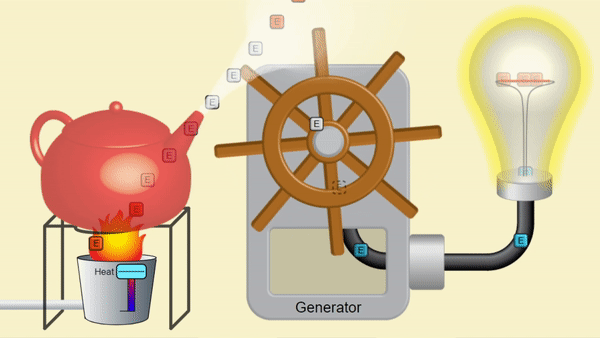
System provided by PhET Interactive Simulations [5]

How does uranium produce electricity?
Uranium produces electricity through the process of fission. Fission is the splitting of atoms, releasing radiation and heat. Once this process is kick-started it creates a chain reaction amongst other atoms. From this reaction, the heat is harnessed to boil water and create steam, which in turn spins a turbine, creating electricity from a generator.
Canada for the last 50+ years has been operating a type of nuclear reactor called a CANDU reactor, which stands for CANadian Deuterium Uranium. The image shown is of the reactor core of a CANDU. What sets it apart from other reactors is a few big advantages:
- Continuous refueling! No need to shut the reactor down to replace fuel
- Able to use natural uranium with no expensive enrichment necessary
- Able to produce medical isotopes for cancer treatment
Explore the different parts of a nuclear reactor in the digital model of a CANDU reactor below: https://energyeducation.ca/3dmodels/Exterior/
Commonly asked questions about Nuclear:
Where are Canada’s reactors located?
Why is Canada so influential in nuclear history?
What happens to the fuel after it leaves the reactor?
Who ensures the safety of Canada’s nuclear sector?
How much does nuclear power cost?
How can nuclear reactors work with renewable energy?
What are SMRs and what exciting possibilities do they offer?
What are the types of nuclear waste and how are they managed?
How is the medical field reliant on the nuclear industry?
How does Canada transport nuclear material?
Citations
- https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/energy-commodities/electricity/report/2017-canadian-renewable-power/province/canadas-renewable-power-landscape-2017-energy-market-analysis-ontario.html
- https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/energy-markets/provincial-territorial-energy-profiles/provincial-territorial-energy-profiles-new-brunswick.html
- https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/our-natural-resources/energy-sources-distribution/nuclear-energy-uranium/7691
- Malkoske, G.R., Norton, J.L., & Slack, J. (2002). Cobalt-60 production in CANDU power reactors. 40 years of nuclear energy in Canada, (p. 96Megabytes). Canada: Canadian Nuclear Society.
- https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/energy-forms-and-changes/latest/energy-forms-and-changes_en.html
- https://www.opg.com/powering-ontario/our-generation/nuclear/nuclear-power-how-it-works/
